2.1 2022년 전체 주문건, 총 매출, 평균 매출
order_items 테이블에서 2022년도의 전체 주문건수, 총 매출, 평균 매출을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 전체 주문 건수 (total_order_count)
- 판매 금액 합계_(total_sale_price)
- 평균 판매 금액 (avg_sale_price)
select count(order_id) as total_order_count,
sum(sale_price) as total_sale_price,
avg(sale_price) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where extract(year from created_at) = 2022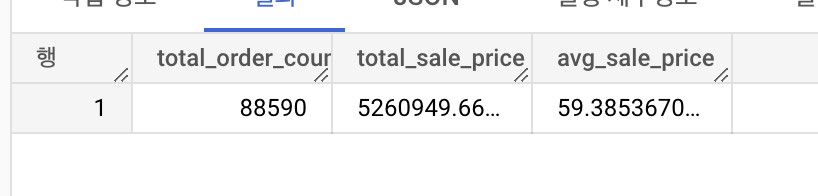
2.2 월별
2.2.1 2022년 월별 주문건, 총 매출, 평균 매출
order_items 테이블에서 2022년도의 월별 주문건수, 총 판매금액, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 월(month)
- 주문 건수 (total_order_count)
- 판매 금액 합계 (total_sale_price)
- 평균 판매금액 (avg_sale_price)
정렬 순서
- 월(month) 오름차순
select extract(month from created_at) as month,
count(id) as total_order_count,
sum(sale_price) as total_sale_price,
avg(sale_price) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where extract(year from created_at) = 2022
group by month
order by month
- 처음에 틀린 이유 -> group by은 extract(month from create_at) 으로 했는데 order by 는 month만 함
근데 왜 틀리지?
2.2.2 모든 연도의 월별 주문건, 총 매출, 평균 매출
order_items 테이블에서 2022연도까지의 모든연도의 주문문건수, 총 판매금액, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 연도(year)
- 주문 건수 (total_order_count)
- 판매 금액 합계 (total_sale_price)
- 평균 판매금액 (avg_sale_price)
정렬 순서
- 월(month) 오름차순
select
extract(month from created_at) as month,
count(distinct order_id) as total_order_count,
round(sum(sale_price), 2) as total_sale_price,
round(avg(sale_price), 2) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where EXTRACT(YEAR FROM created_at) <= 2022
group by month
order by month;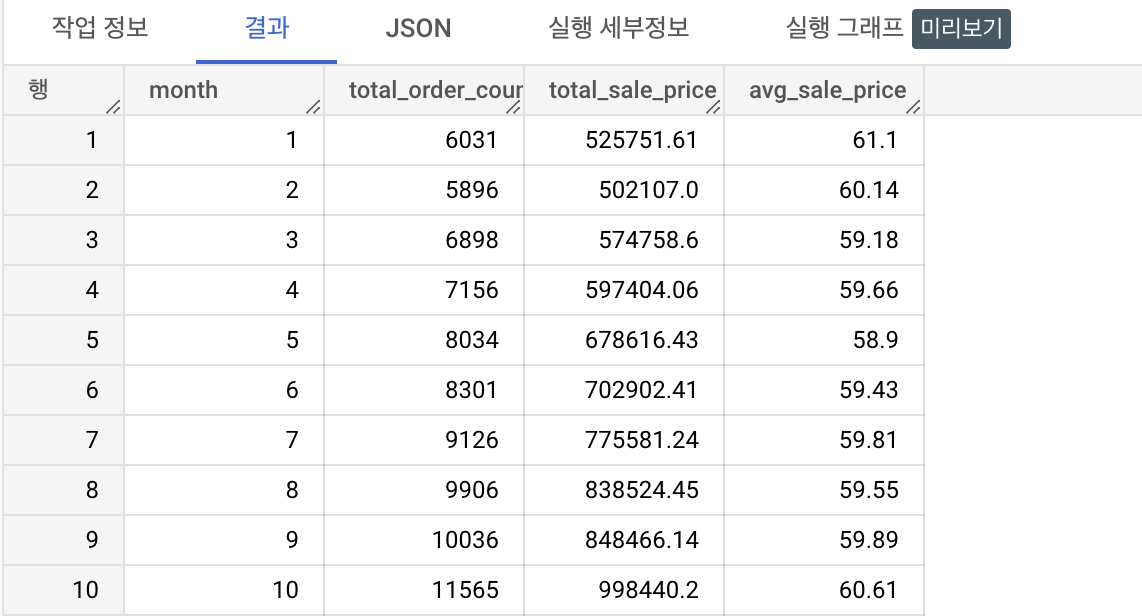
2.2.3 2022년도와 2022년도 이하 모든연도의 월별 주문건수, 판매금액합계, 평균판매금액
order_items 테이블에서 월별 주문건수, 판매금액합계, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 월(month)
- 2022년도의 월 주문건수 (order_count_2022)
- 모든 연도의 월 주문건수 (order_count_total)
- 2022년도의 월 판매금액 합계 (sum_sale_price_2022)
- 모든 연도의 월 판매금액 합계 (sum_sale_price_total)
- 2022년도의 월 평균판매금액 (avg_sale_price_2022)
- 모든 연도의 월 평균 판매금액 (avg_sale_price_total)
정렬 순서
- 월(month) 오름차순
WITH sale_2022 AS
(
SELECT
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM CREATED_AT) AS month,
COUNT(DISTINCT ORDER_ID) AS total_order_count,
ROUND(SUM(SALE_PRICE), 2) AS total_sale_price,
ROUND(AVG(SALE_PRICE), 2) AS avg_sale_price
FROM `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM CREATED_AT) = 2022
GROUP BY MONTH
ORDER BY MONTH
),
sale_total AS (
SELECT
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM CREATED_AT) AS month,
COUNT(DISTINCT ORDER_ID) AS total_order_count,
ROUND(SUM(SALE_PRICE), 2) AS total_sale_price,
ROUND(AVG(SALE_PRICE), 2) AS avg_sale_price
FROM `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM created_at) <= 2022
GROUP BY MONTH
ORDER BY MONTH
)
SELECT
t1.month,
t1.total_order_count as order_count_2022,
t2.total_order_count as order_count_total,
t1.total_sale_price as sum_sale_price_2022,
t2.total_sale_price as sum_sale_price_total,
t1.avg_sale_price as avg_sale_price_2022,
t2.avg_sale_price as avg_sale_price_total
FROM sale_2022 t1
JOIN sale_total t2 ON t1.month = t2.month
order by month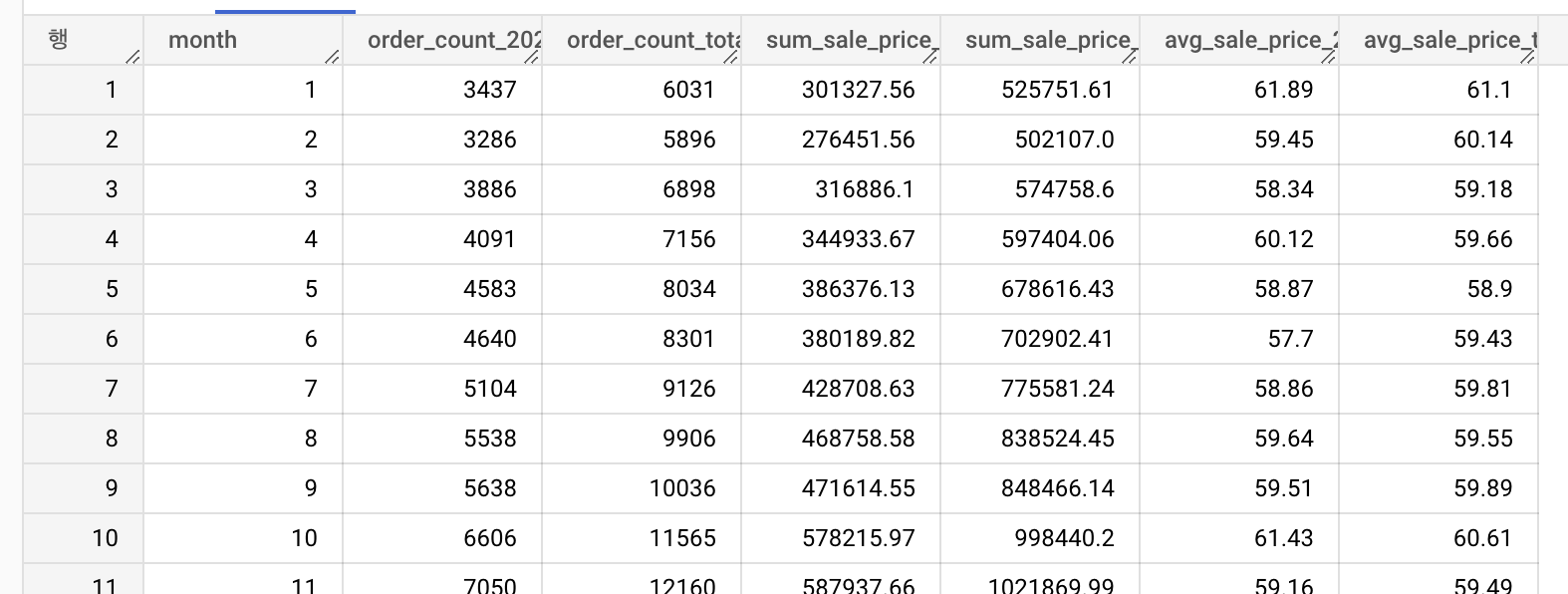
2.3 분기별(계절별)
2.3.1 2022년 분기별(계절별) 주문건, 총 매출, 평균 매출
order_items 테이블에서 2022년도의 분기별 주문건수, 총 판매금액, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 분기(quarter)
- 주문 건수 (total_order_count)
- 판매 금액 합계 (total_sale_price)
- 평균 판매금액 (avg_sale_price)
정렬 순서
- 분기(quarter) 오름차순
select
extract(quarter from created_at) as quarter,
count(id) as total_order_count,
round(sum(sale_price), 2) as total_sale_price,
round(avg(sale_price), 2) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where extract(year from created_at) = 2022
group by quarter
order by quarter
2.3.2 2022년도 이하 모든 연도의 분기별(계절별) 주문건, 총 매출, 평균 매출
order_items 테이블에서 2022년도 이하 모든 연도의 분기별 주문건수, 총 판매금액, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 분기(quarter)
- 주문 건수 (total_order_count)
- 판매 금액 합계 (total_sale_price)
- 평균 판매금액 (avg_sale_price)
정렬 순서
- 분기(quarter) 오름차순
select
extract(quarter from created_at) as quarter,
count(id) as total_order_count,
round(sum(sale_price), 2) as total_sale_price,
round(avg(sale_price), 2) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where extract(year from created_at) <= 2022
group by quarter
order by quarter
2.3.3 2022년도와 2022년도 이하 모든 연도의 분기별 주문건수, 판매금액합계, 평균판매금액
order_items 테이블에서 분기별 주문건수, 판매금액합계, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 분기(quarter)
- 2022년도의 분기 주문건수 (order_count_2022)
- 모든 연도의 분기 주문건수 (order_count_total)
- 2022년도의 분기 판매금액 합계 (sum_sale_price_2022)
- 모든 연도의 분기 판매금액 합계 (sum_sale_price_total)
- 2022년도의 분기 평균판매금액 (avg_sale_price_2022)
- 모든 연도의 분기 평균 판매금액 (avg_sale_price_total)
정렬 순서
- 분기(quarter) 오름차순
with sale_2022 as (
select
extract(quarter from created_at) as quarter,
count(id) as total_order_count,
round(sum(sale_price), 2) as total_sale_price,
round(avg(sale_price), 2) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where extract(year from created_at) = 2022
group by quarter
order by quarter
),
sale_all as (
select
extract(quarter from created_at) as quarter,
count(id) as total_order_count,
round(sum(sale_price), 2) as total_sale_price,
round(avg(sale_price), 2) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where extract(year from created_at) <= 2022
group by quarter
order by quarter
)
select
t1.quarter,
t1.total_order_count as order_count_2022,
t2.total_order_count as order_count_total,
t1.total_sale_price as sum_sale_price_2022,
t2.total_sale_price as sum_sale_price_total,
t1.avg_sale_price as avg_sale_price_2022,
t2.avg_sale_price as avg_sale_price_total
from sale_2022 as t1
join sale_all as t2 on t1.quarter = t2.quarter
order by quarter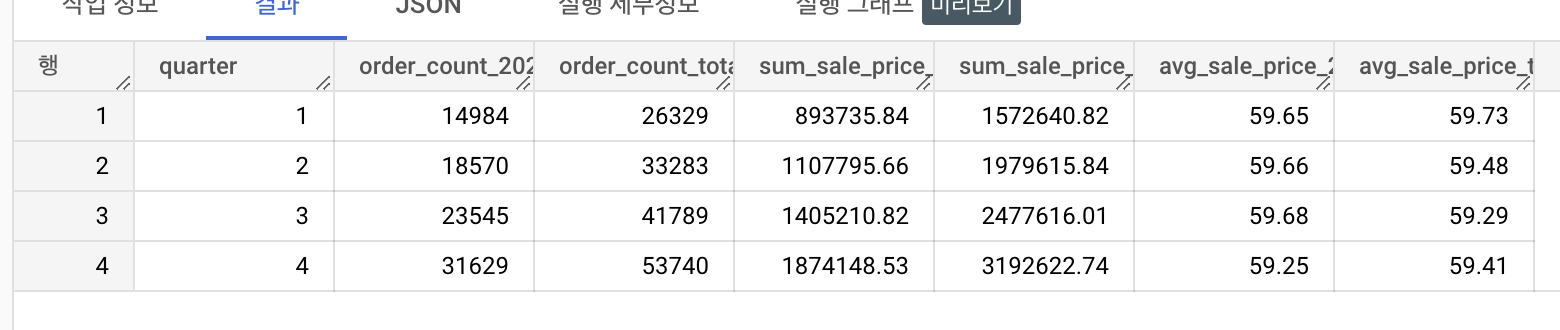
2.4 요일별
2.4.1 2022년 요일별 주문건, 총 매출, 평균 매출
order_items 테이블에서 2022년도의 요일별 주문건수, 총 판매금액, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 요일번호(day_number)
- 요일(day)
- 주문 건수 (order_count)
- 판매 금액 합계 (total_sale_price)
- 평균 판매금액 (avg_sale_price)
정렬 순서
- 요일번호(day_number) 오름차순
select
extract(dayofweek from created_at) as day_number,
format_date('%a', created_at) as day,
count(distinct(id)) as total_order_count,
round(sum(sale_price), 2) as total_sale_price,
round(avg(sale_price), 2) as avg_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
where extract(year from created_at) = 2022
group by day_number, day
order by day_number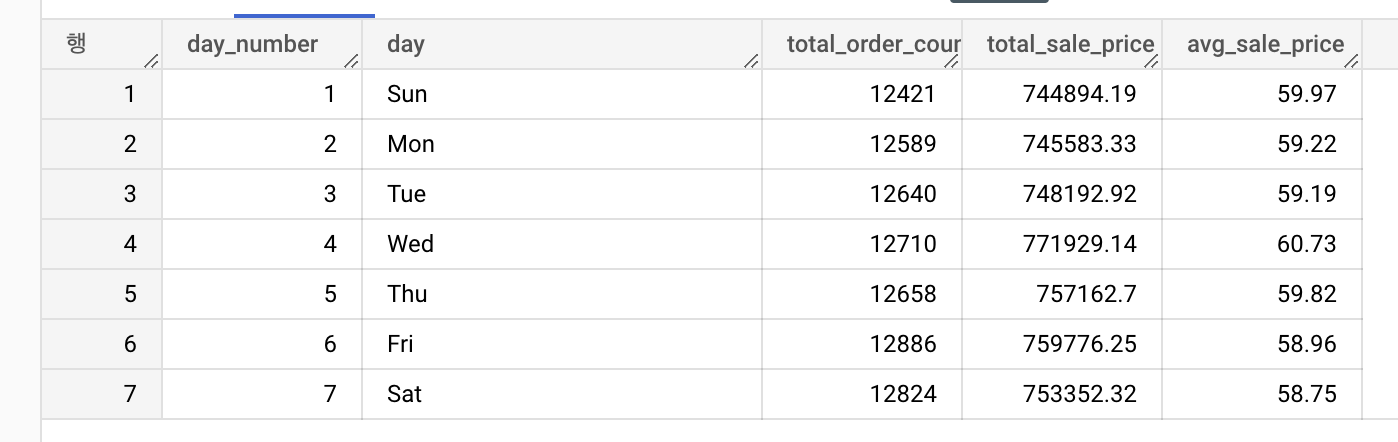
%A 로 하면 Monday 이렇게 길게 나옴
2.8 브랜드별
2.8.1 브랜드별 전체 주문건, 2022년 주문건 및 주문건 순위
order_items 테이블과 products 테이블에서 2022년도와 2022년도 이하 모든 연도의 브랜드별 주문건수와 주문건수 순위 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 브랜드(brand)
- 전체 주문 건수 (order_count_total)
- 2022년도 주문 건수 (order_count_2022)
- 2022년도 기준 주문건수 순위 (rank_2022)
정렬 순서
- 2022년도 기준 주문건수 순위 (rank_2022) 오름차순
with brand_order_count_all as (
select
t2.brand,
count(t1.id) as order_count
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items` t1
left join `thelook_ecommerce.products` t2 on t1.product_id = t2.id
where extract(year from t1.created_at) <= 2022
group by brand
), brand_order_count_2022 as (
select
t2.brand,
count(t1.id) as order_count
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items` t1
left join `thelook_ecommerce.products` t2 on t1.product_id = t2.id
where extract(year from t1.created_at) = 2022
group by brand
),
brand_order_count_list as (
select
t1.brand,
t1.order_count as order_count_total,
t2.order_count as order_count_2022
from brand_order_count_all t1
left join brand_order_count_2022 t2 on t1.brand = t2.brand
)
select
brand,
order_count_total,
order_count_2022,
rank() over( order by order_count_2022 desc ) as rank_2022
from brand_order_count_list
order by order_count_2022 descselect
brand,
count(t1.id) as order_count_total,
count(case when extract(year from t1.created_at) = 2022 then t1.id end) as order_count_2022,
rank() over(order by count(case when extract(year from t1.created_at) = 2022 then t1.id end) desc) as rank_2022
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items` t1
left join `thelook_ecommerce.products` t2 on t1.product_id = t2.id
where extract(year from t1.created_at) <= 2022
group by brand
order by rank_2022
2.8.2 브랜드별 전체 총 매출, 2022년 총 매출 및 매출 순위
order_items 테이블과 products 테이블에서 2022년도와 2022년도 이하 모든 연도의 브랜드별 판매금액 합계, 평균 판매금액을 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 브랜드(brand)
- 전체 판매금액 합계 (sum_sale_price_total)
- 2022년도 판매금액 합계 (sum_sale_price_2022)
- 2022년도 기준 판매금액 합계 순위 (rank_2022)
정렬 순서
- 2022년도 기준 판매금액 합계 순위 (rank_2022) 오름차순
with brand_orders as (
select
t2.brand,
round(sum(t1.sale_price), 2) as sum_sale_price_total,
round(sum(case when extract(year from created_at) = 2022 then t1.sale_price end), 2) as sum_sale_price_2022
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items` t1
join `thelook_ecommerce.products` t2 on t1.product_id = t2.id
where extract(year from created_at) <= 2022
group by brand
)
select
brand,
sum_sale_price_total,
sum_sale_price_2022,
rank() over(order by sum_sale_price_2022 desc) as rank_2022
from brand_orders
order by rank_2022
2.9 카테고리별
2.9.1 카테고리별 전체 주문건, 2022년 주문건 및 주문건 순위
order_items 테이블과 products 테이블에서 2022년도와 2022년도 이하 모든 연도의 카테고리별 주문건수와 준문건수 순위 조회해보세요.
조회 항목
- 카테고리(category)
- 전체 주문 건수 (order_count_total)
- 2022년도 주문 건수 (order_count_2022)
- 2022년도 기준 주문건수 순위 (rank_2022)
정렬 순서
- 2022년도 기준 주문건수 순위 (rank_2022) 오름차순
with category_order_count as (
select
t2.category,
count(t1.order_id) as order_count_total,
count(case when extract(year from t1.created_at) = 2022 then t1.order_id end) as order_count_2022
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items` t1
join `thelook_ecommerce.products` t2 on t1.product_id = t2.id
where extract(year from t1.created_at) <= 2022
group by category
order by order_count_total desc
)
select
category,
order_count_total,
order_count_2022,
rank() over(order by order_count_2022 desc) as rank_2022
from category_order_count
order by rank_2022 asc
3.1 VVIP 구매 고객 목록
3.1.1 VVIP
VVIP는 구매 금액 합계 상위 0.1% 유저입니다. VVIP 유저 목록을 구하기 위해 유저아이디별 주문수, 판매금액합계, 판매금액 합계 순위를 조회하세요.
조회 항목
- 유저 ID (user_id)
- 주문수 (order_count)
- 주문 아이템 수 (order_item_count)
- 판매금액합계 (sum_sale_price)
- 판매금액합계 순위 (rank_sale_price)
- 판매금액합계 퍼센트 랭크 (percent_rank_sale_price) : 소수점 4자리까지 표시 + ‘%’
- 예) 0.0012%
정렬 순서
- 판매금액합계 순위 (rank_sale_price) 오름차순
with sale_list as (
select user_id,
count(distinct(order_id)) as order_count,
count(id) as order_item_count,
sum(sale_price) as sum_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
group by user_id
order by sum_sale_price desc
)
select
user_id,
order_count,
order_item_count,
sum_sale_price,
rank() over(order by sum_sale_price desc) as rank_sale_price,
trunc(percent_rank() over (order by sum_sale_price desc) * 100, 4) || '%' as percent_rank_sale_price
from sale_list
order by rank_sale_price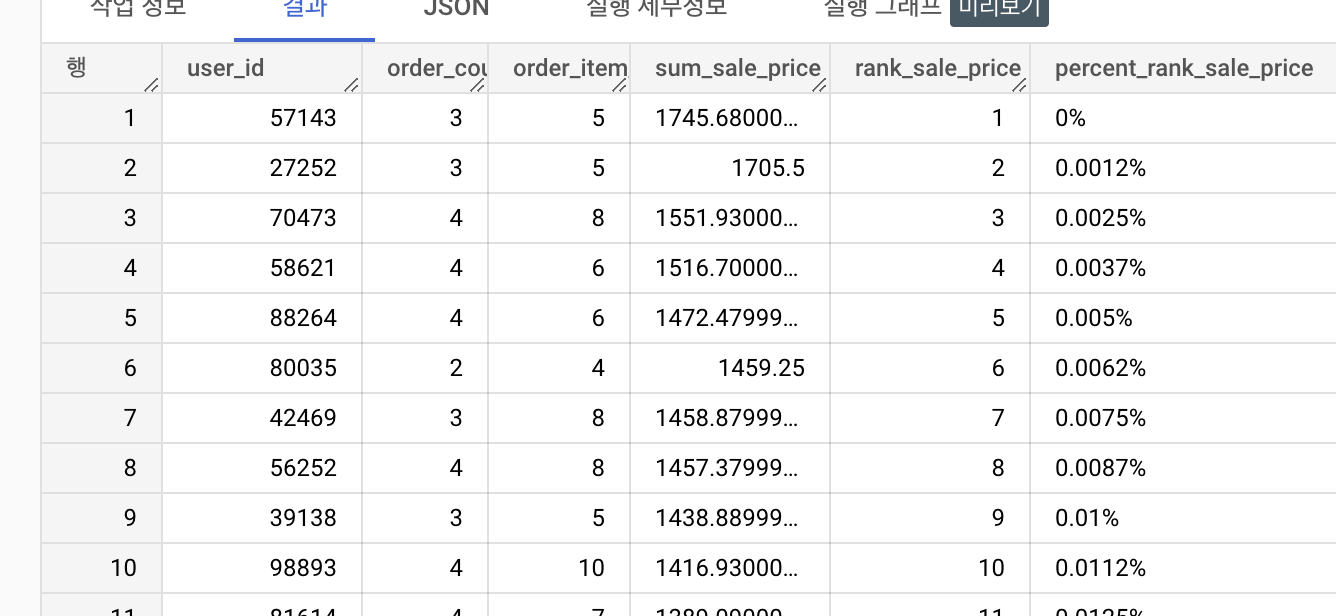
- 내가 한 거
select
user_id,
count(distinct order_id) as order_count,
count(id) as order_item_count,
round(sum(sale_price),2) as sum_sale_price,
rank() over(order by sum(sale_price) desc) as rank,
trunc(percent_rank() over(order by sum(sale_price) desc)*100,4)||'%' as percent_rank_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
group by user_id
order by rank-> 남이 한 거 : 이게 낫다
이렇게 쉬운 방법ㅂ이 있는데 왜 그렇게 한거지?
WITH를 쓰는 것과 쓰지 않는 것 중 속도 측면에서 어느 것이 더 효율적?
-> 쓰지 않는 것이 속도 측면에서 더 효율적일 가능성이 큼 DBMS는 옵티마이저가 쿼리를 분석해서 최적의 실행경로를 만들고 실행해주기 때문에 의도적으로 2번으로 나눈 with보다는 쿼리가 하나로 되어있는것이 최적화될 가능성이 더 크기 때문
3.1.2 VVIP 고객의 주문, 구매 분석
- VVIP의 주문 횟수는 몇회 일까?
- VVIP의 주문 상품 개수는 몇개 일까?
- VVIP의 구매 금액 합계는 얼마 이상 일까?
매출금액 순위 상위 0.1% 유저(VVIP)의 평균주문건수, 평균 주문 아이템 건수, 평균 판매가격, 최소구매횟수, 최소 구매금액을 조회하세요.
조회 항목
- 평균 주문 수 (avg_order_count)
- 평균 주문 아이템 수 (avg_order_item_count)
- 평균 판매 금액 (avg_sum_sale_price)
- 최소 주문 횟수 (min_order_item_count)
- 최소 판매 금액 합계 (min_sum_sale_price)
with sale_list as (
select user_id,
count(distinct(order_id)) as order_count,
count(id) as order_item_count,
sum(sale_price) as sum_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
group by user_id
order by sum_sale_price desc
),
order_list as (
select
user_id,
order_count,
order_item_count,
sum_sale_price,
rank() over(order by sum_sale_price desc) as rank_sale_price,
trunc(percent_rank() over (order by sum_sale_price desc) * 100, 4) as percent_rank_sale_price
from sale_list
order by rank_sale_price )
select
avg(order_count) as avg_order_count,
avg(order_item_count) as avg_order_item_count,
avg(sum_sale_price) as avg_sum_sale_price,
min(order_item_count) as min_order_item_count,
min(sum_sale_price) as min_sum_sale_pice
from order_list
where percent_rank_sale_price <= 0.1
- group by 안 해서 한 줄만
3.2.2 유저레벨링(유저 등급) 적용
총 구매금액을 기준으로 10개의 등급으로 나눈 후 각 등급에서 총 구매금액의 최소 금액을 조회해 보도록 하겠습니다.
- 유저별 판매금액 합계 목록을 조회 합니다.
조회 항목
- 유저ID (user_id)
- 판매금액합계 (sum_sale_price)
select
user_id,
sum(sale_price) as sum_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
group by user_id
order by sum_sale_price desc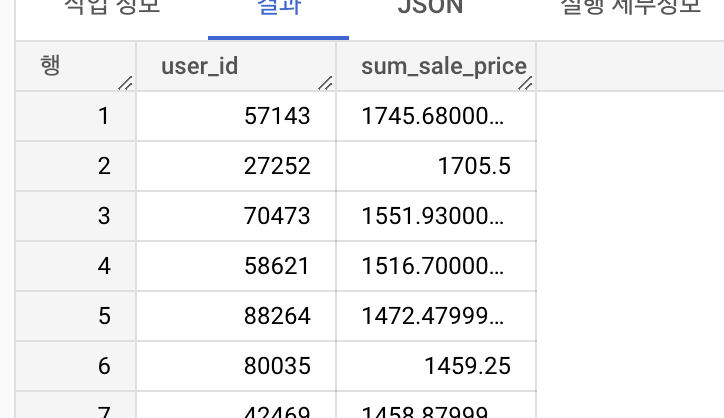
유저별 판매금액 합계기준 10단계 ntile을 구합니다.
조회 항목
- 유저 ID (user_id)
- 판매금액 기준 누적분포 (cume_dist_sum_sale_price)
- ntile
with user_price as (
select
user_id,
sum(sale_price) as sum_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
group by user_id
order by sum_sale_price desc )
select
user_id,
sum_sale_price,
cume_dist() over (order by sum_sale_price desc) * 100 as cume_dist_sum_sale_price,
ntile(10) over (order by sum_sale_price desc) ntile
from user_price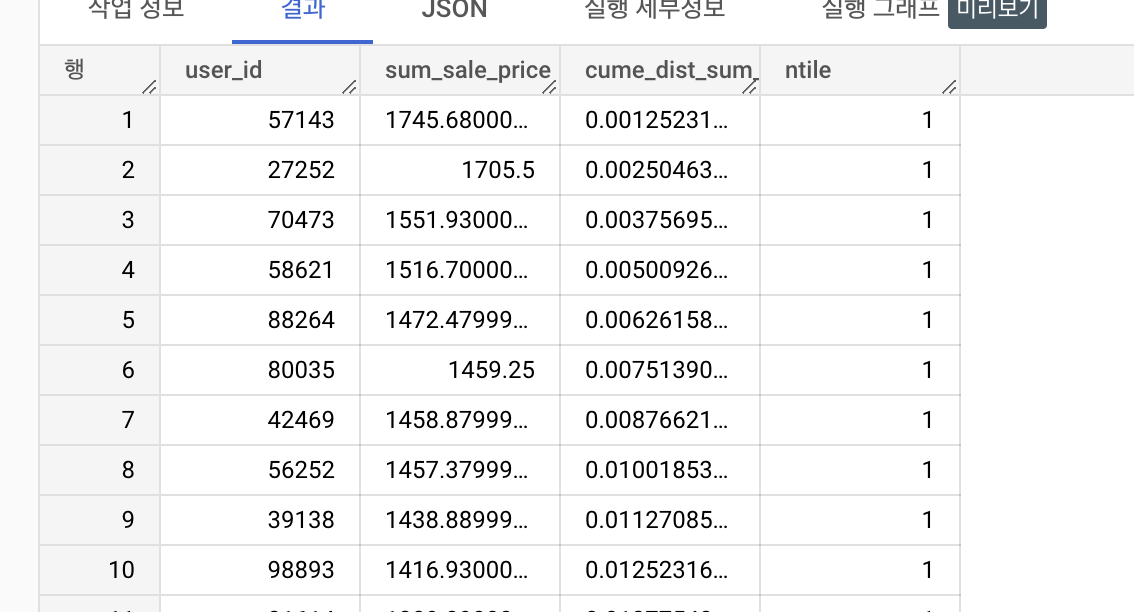
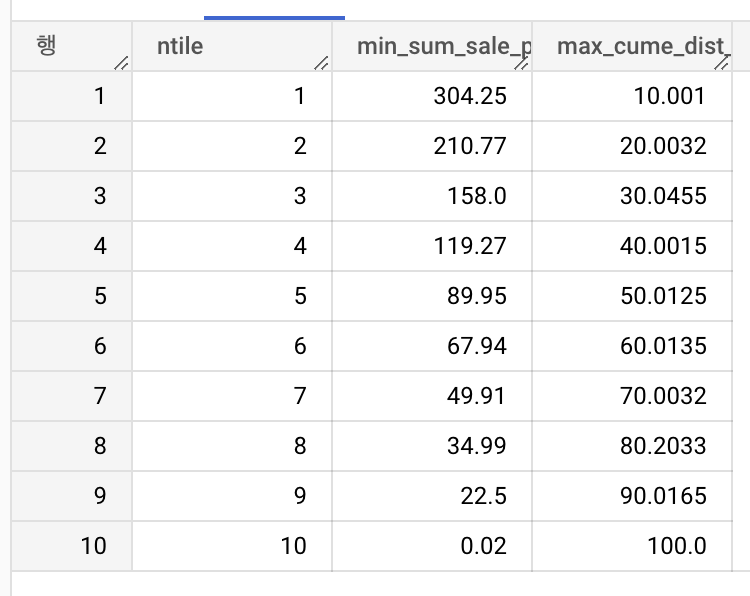
각 ntile별 최소판매금액
조회 항목
- ntile
- 최소 판매 금액 합계 (min_sum_sale_price)
- 누적분포 최대값 (max_cume_dist_sum_sale_price)
with user_price as (
select
user_id,
round(sum(sale_price), 2) as sum_sale_price
from `thelook_ecommerce.order_items`
group by user_id
order by sum_sale_price desc ),
dume_list as
(select
user_id,
sum_sale_price,
trunc(cume_dist() over (order by sum_sale_price desc) * 100, 4)as cume_dist_sum_sale_price,
ntile(10) over (order by sum_sale_price desc) as ntile
from user_price
)
select
ntile,
min(sum_sale_price) as min_sum_sale_price,
max(cume_dist_sum_sale_price) as max_cume_dist_sum_sale_price
from dume_list
group by ntile- 각 구간의 경계
'AI SCHOOL > SQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SQL] WITH / 서브쿼리 연습문제 - 1 (0) | 2023.02.02 |
|---|---|
| [SQL] WITH / 서브쿼리 (0) | 2023.02.02 |
| [SQL] 집합 연습문제 (0) | 2023.01.27 |
| [SQL] 집합 (0) | 2023.01.27 |
| [SQL] JOIN 연습문제 (0) | 2023.01.26 |